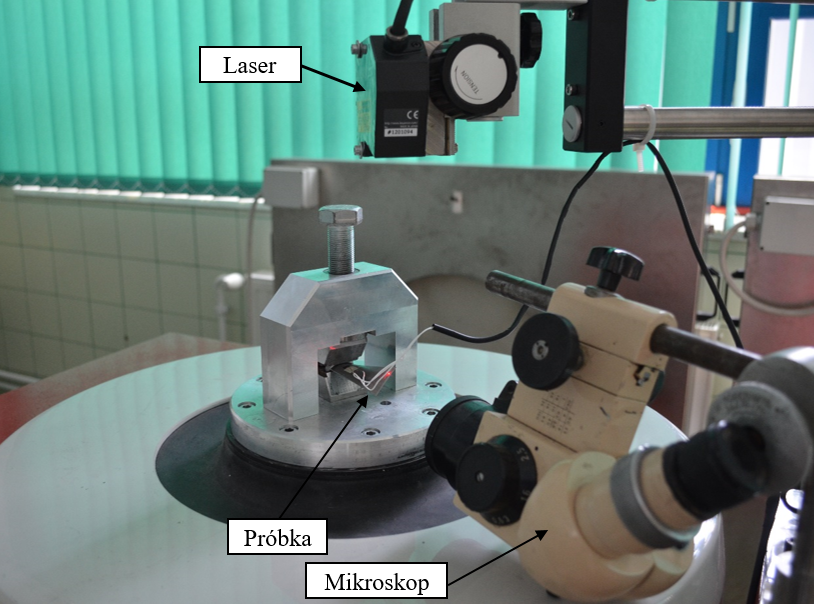
Crack measurement
Equipment for observation and documentation of the crack propagation in compressor blades.
Equipment allows to precisely define the shape of the damage. It is possible to perform measurements and calculate the damage geometry surface area. The measurements can be done only in one plane. The image analysis in the first phase will also perform analysis on two-dimensional pictures. Operating parameters of the stereoscopic microscope:

- → Binocular microscope head,
- → Zoom - 0,8,
- → Eyepiece magnification - 10x,
- → Lens magnification - 1x,
- → Manual control of the stand,
- → halogen lighting.

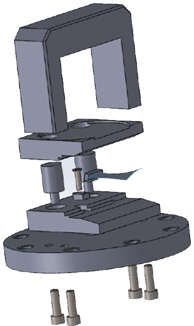
Equipment instrumentation
Hydraulic handle for the fatigue testing
In order to ensure reproducibility of the results of the high cycle fatigue tests of the turbine engine compressor blade it was designed set of jaws to ensure reproducible in terms of the orientation of the blade mounting in the lock. For the jaws it was designed and manufactured grip for permanent attachment of a vibrating table with the possibility of stepless load.
In order to obtain infinitely variable load hydraulic actuator was applied. Stepless load can be applied thanks to the use of the feed pump for the actuator. To ensure the application and maintaining the value of the task force it was applied the manometer and the valve blocking the force set value.
To ensure the reproducibility of the sample holder assembly and ensure a reliable, repeatable loading during research trials contributes to obtaining accurate results of fatigue tests.
Both in the design and implementation of the handle focused on the fact that a universal handle, so that could be used to test a wide range of frequency.
Universal handle gives the opportunity to exchange jaw while keeping the rest of the design and extortion.


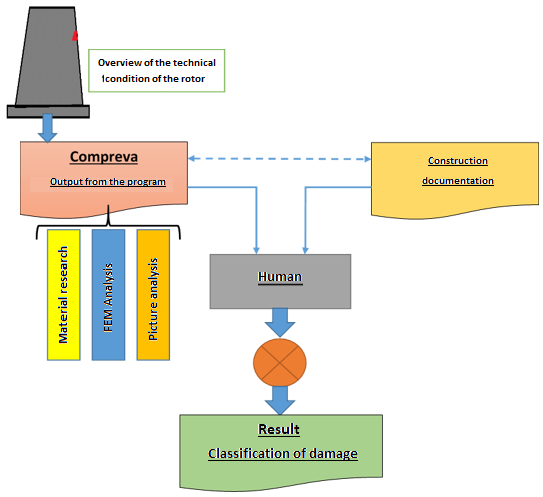
The geometry defect detection...
Analysis of geometry and photographic documentation of damage.
The test equipment for observation and documentation of damage for the compressor blades consists of the following components:
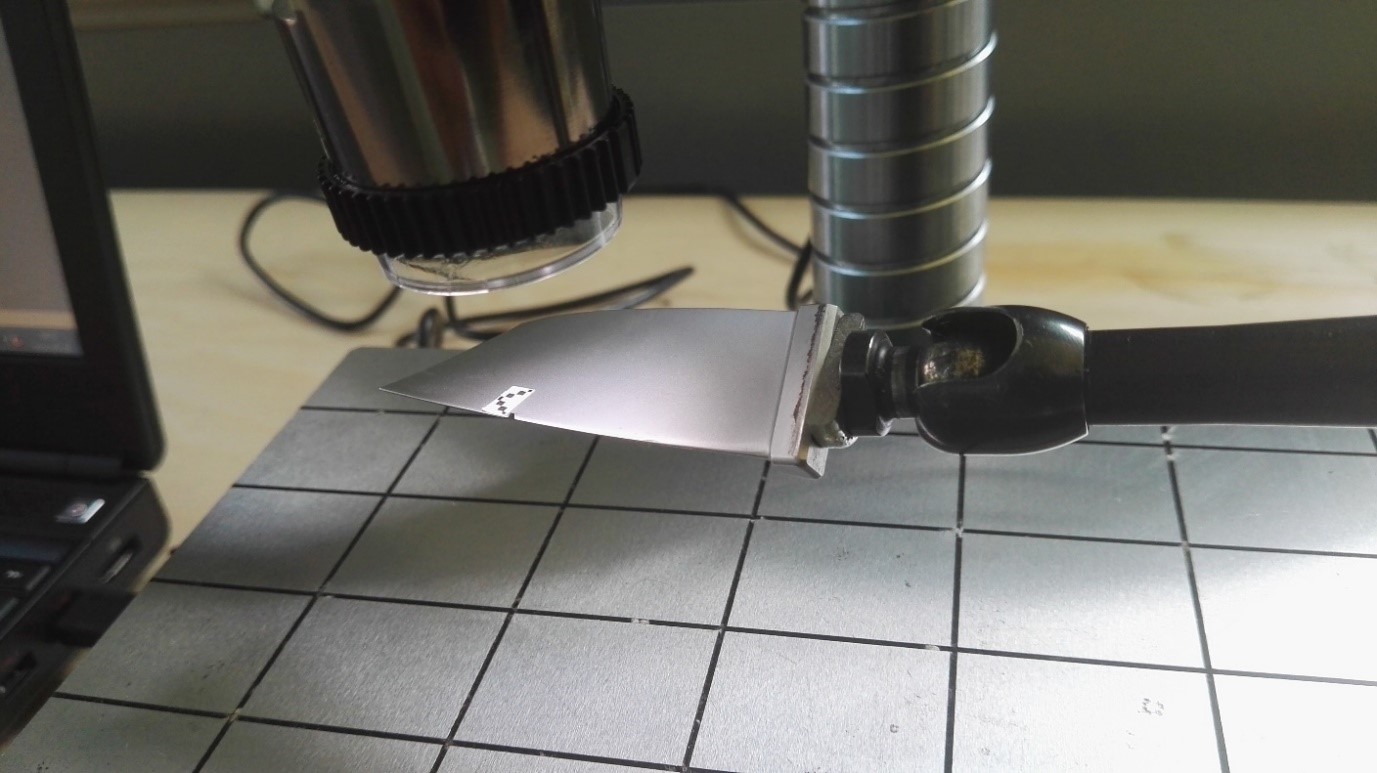

- ★ Digital microscope – Dino-Lite Edge AM7515MZT,
- ★ Measuring stand with the height adjustment,
- ★ Magnetic stand NOGA MG 61030,
- ★ Workstation – laptop,
- ★ Software – DinoCapture 2.0
Microscope Dino-Lite Edge AM7515MZT is equipped with a digital archiving system. Control of the microscope is performed using DinoCapture 2.0. The microscope head has a smooth change of magnification - 20x to 220x. Based images have a resolution of 5 Megapixels (2592x1944 pixels). The microscope has a flexible control of the LED, which allows appropriate adjustment of the lighting test vane.
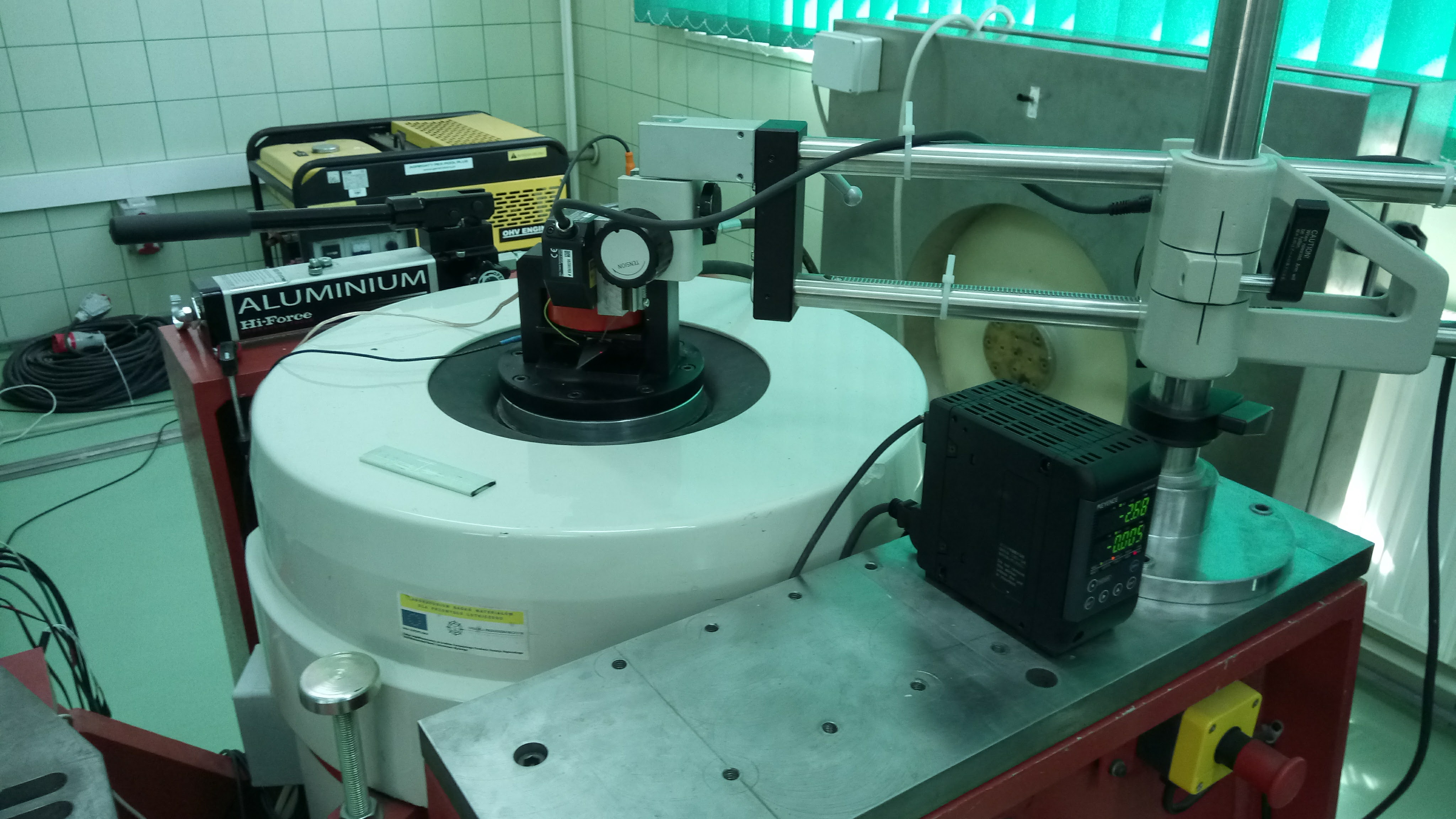


Fatigue tests...
Research equipment for fatigue tests.
The test equipment for fatigue testing consists of the following components:
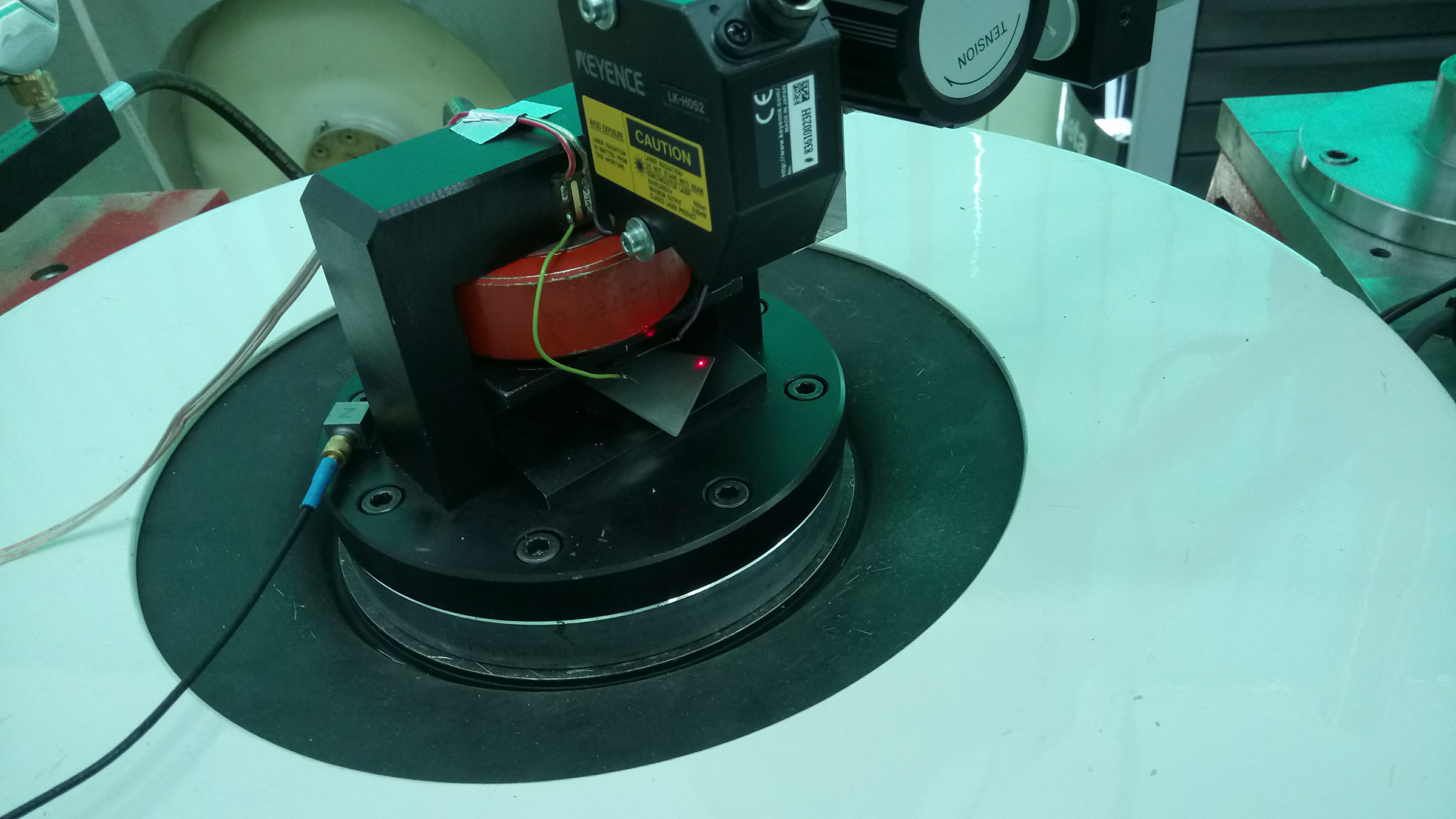

- ★ Electrodynamic inductor,
- ★ Climatic chamber,
- ★ Power amplifier,
- ★ Computer control system.
The fatigue test control system was developed using National Instruments' control and measurement cards and the Labview development environment. The computer program controls the operation of the electrodynamic inductor and ensures that the required amplitude and frequency of the vibration of the head is achieved. Allows the sample to be tested for resonance vibration. The constant value of the vibration amplitude of the blade blade is a condition of its constant dynamic load during the fatigue test.

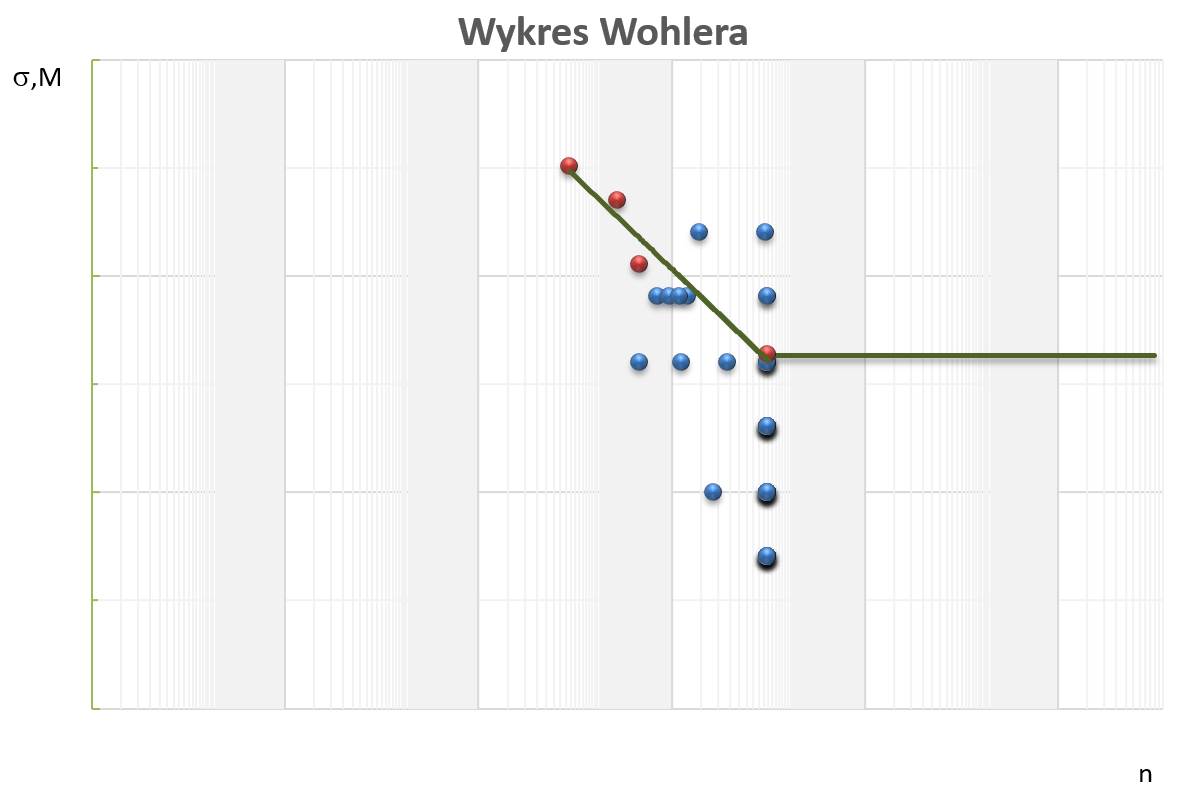
Fatigue curve...
Method of determining the fatigue curve using the airplane compressor stage I blades
The average durable fatigue strength at room temperature was determined using the cracking method.
Samples in the form of an airplane compressor blade fixed in the vibration motor holder were subjected to a cyclic bend with a specified sigma1 stress value at a specified base number of cycles n. In the absence of fracture during the test at the assumed number of cycles n, the sample was subjected to a sigma2 = + Sigma1 deltasigma. The stress value was increased until the sample was cracked.

Vision system...
Vision system for analyzing the size of the air compressor blades defects.
Participants in the ComprEva project took part in the 17th mechatronic design workshop organized by the Chair of Robotics and Mechatronics of the AGH University of Science and Technology held on 1-2 June 2017 in Cracow.
A vision system was developed to analyze the defects of the air compressor blades. The algorithm developed within the research task uses image processing and analysis techniques for detection, localization and assessment of the extent of blade damage. Introducing the image of the standard deviation of the surrounding pixels from the input image has also allowed detection of the damage also in the case of bad lighting conditions resulting in light reflections. The applied fractal dimension for blade edge analysis enabled the automatic detection of the damage position. Extraction of the damage to measure its geometry is done by adding a binary image to the convex sheath. The method developed was compared with other image analysis methods. It is also possible to use model projection on an image to determine the scale and location of the damage. The use of the developed measurement tool is to assist aircraft diagnostics using endoscopic cameras.

Milestones...
1. Determine the type of blade damage of the selected compression ratio
Detailed damage characteristics of the blade were made to determine the classification criteria for the assessment of fitness after a collision with a foreign body. Macroscopic examination and observation of damaged blades
Indicates that one or more of its defects have been identified, depending on the scale of the event.
A review and classification of compressor blades fault types for two types of aircraft engines - the engine
Helicopter (PZL-10W) and turboprop engine (TWD-10B). The presence of blisters was found with a degree of damage
Preventing further exploitation. Analysis of the results of the review shows that: the blade of the 1st stage of the compressor
Damaged most often, damage occurs on all parts of the blade blade: leading edge and raft,
The ridge and the trough of the shoulder and the top of the shoulder.

2. Development of mathematical models of compressor blades
Discrete elements using quadratic features with a square shape function "TET" were used.  Elements of this type allow to obtain the accuracy of the obtained results of numerical analysis comparable to hexagonal elements with square shape function "HEX" (the advantage of the "HEX" elements is the possibility of using fewer elements for a given geometry).
Discrete model was made in ANSYS Meshing module.
Elements of this type allow to obtain the accuracy of the obtained results of numerical analysis comparable to hexagonal elements with square shape function "HEX" (the advantage of the "HEX" elements is the possibility of using fewer elements for a given geometry).
Discrete model was made in ANSYS Meshing module.
3. Determination of fatigue strength of blades without damage
Fatigue tests under high cycle conditions were carried out for 16-blade blades of the third stage of the engine compressor
air. The blades were tested to determine their high-strength fatigue strength. In nine paddles
Compressors have been damaged to compare their strength with resistance without damage. The research was carried out to verify the MES models. Two were used
Method: excite the vane on the vibrating table to its first form of vibration. It was found that
The results obtained by experimental methods and the FEM method do not differ from one another for individual cases
Damage more than 10%. Similar differences can be seen between the individual blades examined by a particular method.
4. Development of an algorithm to classify defects
Seven automatic algorithms have been developed for analyzing compressor blades and one manual processing algorithm. All algorithms have been tested on test blades by the end of 2016, ie 105
shoulders. Shoulders were damaged in all areas and the lesions had different shapes.
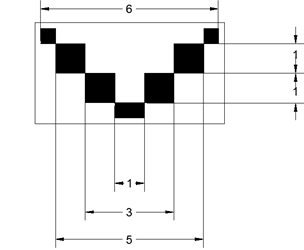
Every paddle before the shot was damaged at a specific location and the damage had the appropriate shape. In addition, a geometric pattern in the form of a checkerboard was attached to the shoulders. As a result, automatic image analysis functions have the ability to convert pixels into metric units. All algorithms described need scaling of the magnitude of the damage, that is, converting the data obtained in pixels into metric units. 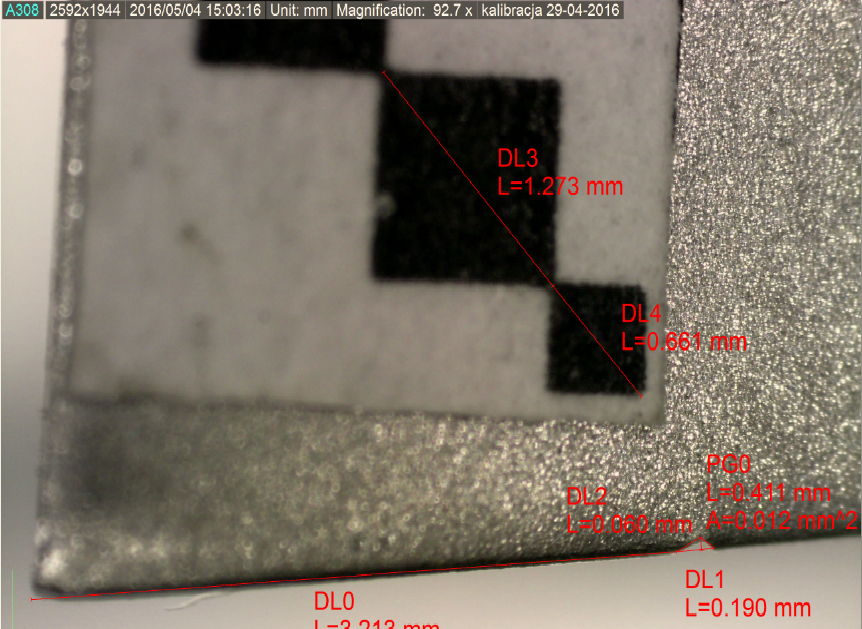

Product indicators...
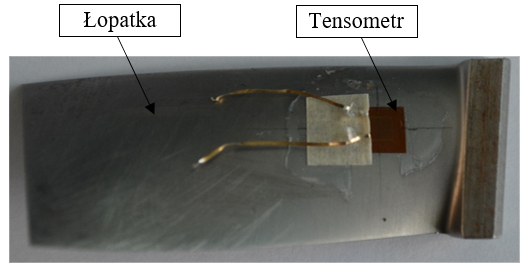
1. Methodology for measuring the amplitude of blade blade vibration during fatigue tests
Verification of applied sensors for measuring the stress on blade blades and analysis of the effectiveness of accepted methods of measuring the displacement of the tip of the vibrating blade of the blade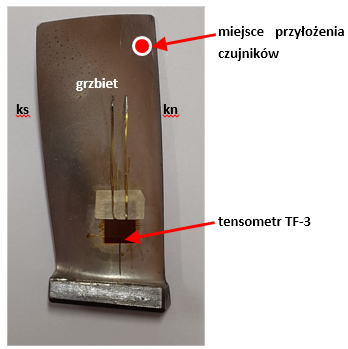
2. Information Base on fatigue strength of a group of compressed blade vanes
A database containing information characterizing all the blades studied during fatigue tests was created. The information was collected as a database file and placed on the server.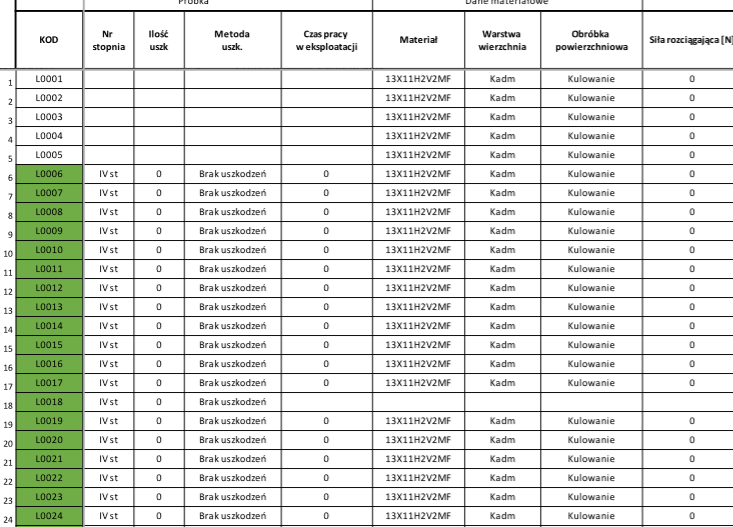
3. Algorithm to assist in analyzing compressor blades damage images
8 algorithms have been developed to support image analysis of compressor blades damage. The programs have been tested on blade images containing three types of damage. The limitations of accepted solutions and suggestions for improving algorithms are discussed .
.
4. Information base on types of damage to the compressor blades resulting from the operation
OThere was a database of information on the types of damage to the compressor caps produced in operation. It describes, among others. Number of defects, types of damage, places of damage and their size.

ComprEva - press releases...
LIDER 5
Co-financing received The following projects: new automatic snow estimation system using unmanned aircraft, development of non-invasive method of selection and optimization of intravascular prostheses, innovative construction of resonance cavity of cascade quantum laser and image analysis in classification of airplane compressor blades defects and forecasting their durability.

Numerical calculations...
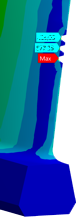
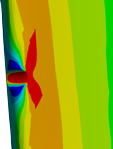
Determination of the stresses of damaged blades with the Finite Elements Method use...
In order to determine the plan to perform the fatigue strength test of damaged blades - the minimum necessary blades should be determined - numerical analyzes were performed. Numerical analyzes were performed for mathematical models that included different types of damage ("V" and "I" types) at different heights of the blade edge and 5 different depths of damage. Several analyzes have also been carried out taking into account multiple failures occurring simultaneously. The results of the analysis in terms of specific frequencies of native vibration and reduced stress distributions significantly facilitated the testing planning process.
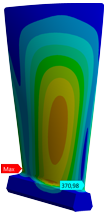
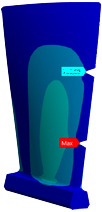

Geometric measurements
The development of an appropriate method for examining the curvilinear surface of a blade has been analyzed several types of measurement of damaged blades.
The Dino-Lite Edge AM7515MZT digital microscope was selected for the project. The resulting image allows you to observe the whole blade of the blade. The results of these measurements may be correlated with the results obtained during image analysis.

They will also validate methodology using image analysis. A measurement error of 0.35% satisfies the design assumptions. The prepared position allows you to precisely determine the shape of the damage. It is possible to perform damage geometry measurements and to calculate the surface area. The special handle keeps the repeatability of measurements. Damage geometry measurements will be transmitted as images and placed on the server.

Database
Development of the database code in the form of a computer file.
The research is based on the developed electronic file according to the file upload scheme on the server. After completing all the required tests on the sample, the research summary record is added to the cumulative research results database.
After material testing has been carried out, the test results database allows for the analysis of the damage that results from the mechanical properties of the blade. The results of this analysis are used for implementation in an image analysis application.

Fatigue strength tests / Numerical analyzes of damaged blades...
Participants of the ComprEva project took part in the XLV School of Materials Engineering organized by the Faculty of Metals and Computational Engineering of the AGH University of Science and Technology in cooperation with the Polish Stereological Society, which took place on 26-29 September 2017 in Rytro.
Zaprezentowano dwa tematy:
1. Fatigue Testing of Damaged Turbine Engine Compressor Blades.
- - Introduction - description of FOD phenomenon and its consequences
- - Method of simulation of blades damage
- - Measurement of damage geometry
- - Fatigue tests
- - Results
- - Summary and plan for further work
2. Numerical analysis of damaged turbine engine compressor blades.
- - Introduction - description of FOD phenomenon and its consequences
- - Stages of numerical calculations
- - CAD Model
- - Finite Element Method FEM, material model
- - Analysis types, boundary condition/initial conditions
- - Analysis of results and summary

Life prediction of aircraft engine compressor blades using a fatigue test and numerical image analysis of their damage
Scientific and research interests mgr inż. Wojciech Obrocki are related to modern methods of diagnostics of aircraft engine compressor blades, with particular emphasis on the initiation of fatigue cracks and the speed of their propagation. He deals with the assessment of damages of the blades from foreign bodies introduced into the engine's air channel. The impact of these damages on the nucleation of cracks and their development during operation, also predicting the life of the blades. He uses the numerical analysis of the image to evaluate these defects.
On October 18, 2017, at the Department of Materials Science at Rzeszów University of Technology, a seminar entitled Forecasting the life span of aircraft engine compressor blades using a fatigue test and numerical analysis of their damage images. During the seminar, Mr. Eng. Wojciech Obrocki gave the results of his research so far. During the discussion after the presentation there were a number of important questions and valuable comments that were taken into account by the author in further progress of his work.